Past Perfect Tense की अवधारणा (Concept of Past Perfect Tense)
Overview
इस लेख में हम अंग्रेजी के एक महत्त्वपूर्ण अध्याय के बारे में जानेंगे - Past Perfect Tense की अवधारणा, in Hindi (हिंदी में)
 नोट
नोटइस अध्याय से सम्बंधित, अन्य विषयों के बारे में जानने के लिए आप हमारे निम्नलिखित लेख पढ़ सकते हैं:
इस लेख में, हम Past Perfect Tense (पास्ट परफेक्ट टेन्स) की अवधारणा, इसके विभिन्न उपयोगों और इस tense का उपयोग करके बनाई जाने वाली विभिन्न वाक्य संरचनाओं के बारे में अध्ययन करने जा रहे हैं।
Past Perfect Tense के उपयोग
उपयोग 1
किसी ऐसी पिछली स्थिति या गतिविधि के बारे में बात करने के लिए हम Past Perfect का उपयोग करते हैं, जो किसी अन्य पिछली स्थिति या गतिविधि से पहले या अतीत में किसी विशेष समय से पहले हुई थी।
यानी, जब दो गतिविधियाँ अतीत में हुईं, तो हम यह दिखाने के लिए past perfect का उपयोग करते हैं कि कौन सी क्रिया दूसरे की तुलना में पहले हुई।
एक उपवाक्य (clause) में Simple Past का और दूसरे में Past Perfect का इस्तेमाल होता है।
आइए कुछ उदाहरण देखें:
Anand realized that the retail broker had duped him.
Anand realized – simple past tense में।
the retail broker had duped him – past perfect tense में।
I had met her in Berlin before we married in 2015.
we married in 2015 – simple past tense में।
I had met her in Berlin – past perfect tense में।
संरचनाएं (Structures)
पैटर्न 1: Subject + had + \(V_3\) + ........ before + Subject + \(V_2\)
Mr. Kapoor had left India before I met Shailey.
पैटर्न 2: By the time + Subject + \(V_2\) + .....+ Subject + had + \(V_3\) +......
By the time Mr. Anand reached home, she had typed all the letters.
पैटर्न 3: Subject + \(V_2\) + ..... + after + Subject + had + \(V_3\) + ......
She told me his name after he had gone.
उपयोग 2
हम जो करना चाहते थे, लेकिन नहीं किया, उसे कहने के लिए भी हम Past Perfect का उपयोग करते हैं।
इस शैली में प्रयुक्त क्रियाएँ (Verbs) – wanted (to), hoped (to), wished (to), expect (to), mean (to), think (about + -ing).
I had wanted to visit Stonehenge before I left England, but my wife is not feeling well.
Mragank had hoped to retire at 50, but his financial conditions didn’t allow him to do so.
 नोट
नोटSubject + had + hoped/wanted/wished/expected/.... + that + Subject + verb ....
काम की पूर्ति न होने की स्थिति में हम perfect tense का उपयोग करते हैं।
Subject + hoped/wanted/wished/expected + ....... + that + Subject + verb +....
हम काम की पूर्ति होने के मामले में simple past tense का उपयोग करते हैं।
I had wanted to be what I am today. (गलत)
I wanted to be what I am today. (सही)
I thought that I would meet you but I couldn’t. (गलत)
I had thought that I would meet you but I couldn’t. (सही)
Past Perfect tense की विभिन्न वाक्य संरचनाएं
हम Present Past Perfect tense में निम्नलिखित सहायक क्रियाओं (helping verbs) का उपयोग करते हैं (subject के पुरुष और संख्या के आधार पर):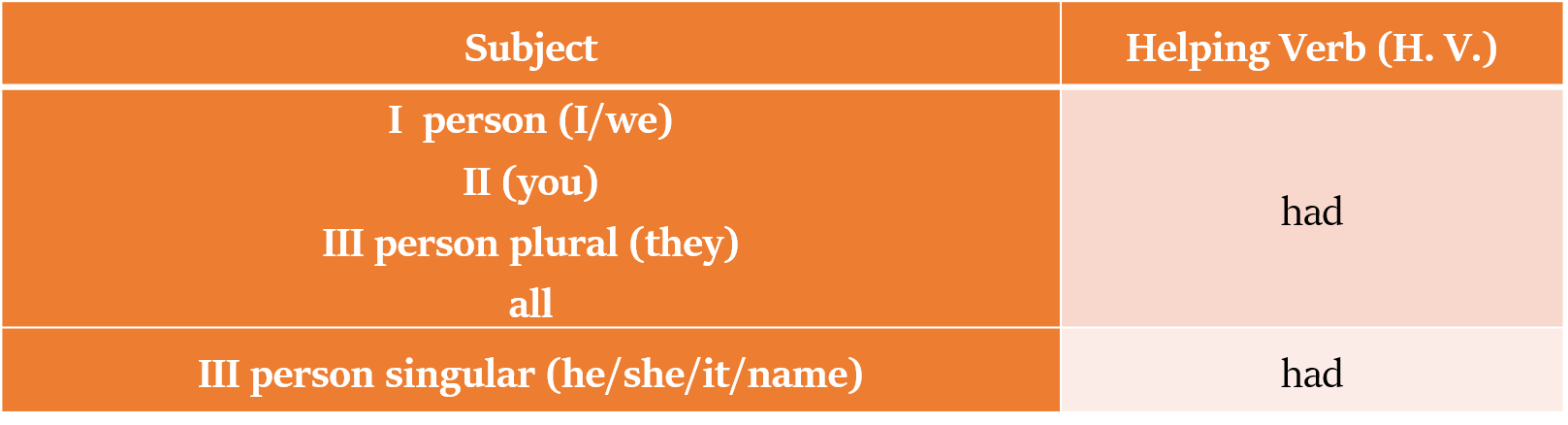
 नोट
नोट'had' हमेशा सहायक क्रिया (helping verb) के रूप में कार्य नहीं करता है। यह मुख्य क्रिया (main verb) के रूप में भी काम कर सकता है।
घोषणात्मक वाक्यों की संरचना (Structure of Declarative sentences)
सकारात्मक घोषणात्मक वाक्य (Affirmative Declarative Sentences)
पैटर्न: Subject + had + \(V_3\) + Object
Aanya had played badminton.
They had played badminton.
नकारात्मक घोषणात्मक वाक्य (Negative Declarative Sentences)
पैटर्न: Subject + had not + \(V_3\) + Object
Aanya had not played badminton.
They had not played badminton.
 नोट
नोटहम had not को hadn't भी लिख सकते हैं|
प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों की संरचना (Structure of Interrogative sentences)
सकारात्मक प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य (Affirmative Interrogative Sentences)
पैटर्न 1: Had + Subject + \(V_3\) + Object?
Had Aanya played badminton?
Had they played badminton?
पैटर्न 2: Wh. family + had + Subject + \(V_3\) + Object?
Where had Aanya played badminton?
Where had they played badminton?
नकारात्मक प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य (Negative Interrogative Sentences)
पैटर्न 1: Had + Subject + not + \(V_3\) + Object?
Had Aanya not played badminton?
Had they not played badminton?
पैटर्न 2: Wh. family + had + Subject + not + \(V_3\) + Object?
Why had Aanya not played badminton?
Why had they not played badminton?
 नोट
नोटकिसी वाक्य में, 'have' के किसी भी रूप के बाद 'had' आ सकता है, जैसे की has had, have had.
Perfect Tense में आपको ऐसे संयोजन बहुत मिलेंगे।
ऐसे मामलों में 'had' मुख्य क्रिया होगी।
I have had enough challenges in this job. (have – helping verb; had – main verb)
He has had his dinner. (has – helping verb; had – main verb)

अतिरिक्त पुस्तकें और उपकरण
यदि आप किताबों के माध्यम से सीखना पसंद करते हैं, या संदर्भ उद्देश्यों के लिए कुछ अच्छी अंग्रेज़ी व्याकरण किताबें चाहते हैं, तो आप हमारा यह लेख पढ़ सकते हैं|