डायरेक्ट कथन को इनडायरेक्ट कथन में बदलने के नियम (Direct Speech ko Indirect Speech mein badalne ke niyam)

Overview
इस लेख में हम अंग्रेजी के एक महत्त्वपूर्ण अध्याय के बारे में जानेंगे - How to convert Direct speech into Indirect speech, in Hindi (हिंदी में)
 नोट
नोटइस अध्याय से सम्बंधित, अन्य विषयों के बारे में जानने के लिए आप हमारे निम्नलिखित लेख पढ़ सकते हैं:
- डायरेक्ट और इनडायरेक्ट कथन क्या होते हैं?
- डायरेक्ट कथन को इनडायरेक्ट कथन में परिवर्तित करने पर काल में परिवर्तन
- घोषणात्मक वाक्यों को इनडायरेक्ट बनाने पर रिपोर्टिंग क्रिया में परिवर्तन
- प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों को इनडायरेक्ट बनाने पर रिपोर्टिंग क्रिया में परिवर्तन
- आदेशसूचक वाक्यों को इनडायरेक्ट बनाने पर रिपोर्टिंग क्रिया में परिवर्तन
- विस्मयादिबोधक और इच्छावाचक वाक्यों को इनडायरेक्ट बनाने पर रिपोर्टिंग क्रिया में परिवर्तन
अर्थ को अक्षुण्ण रखने के लिए, हम direct speech (प्रत्यक्ष भाषण, डायरेक्ट कथन) से indirect speech (अप्रत्यक्ष भाषण, इनडायरेक्ट कथन) में बदलते समय कुछ बड़े बदलाव करते हैं।
आइए उन्हें देखें!
डायरेक्ट से इनडायरेक्ट में बदलना (Conversion from direct speech to indirect speech)
हम रूपांतरण के लिए निम्नलिखित बिंदुओं को ध्यान में रखते हैं:
- समुच्चयबोधक डालना (insertion of conjunction)
- person का परिवर्तन (change of person)
- काल का परिवर्तन (change of tense)
- रिपोर्टिंग क्रिया में परिवर्तन (change in the reporting verb)
- समय या स्थान की अभिव्यक्ति में परिवर्तन (change in the expression of time or place)
- hello, wow, आदि जैसी अनावश्यक चीजों को हटाना (अर्थात वे भाव जो हम आम तौर पर किसी से आमने-सामने बात करते समय उपयोग करते हैं, अर्थात बोली जाने वाली अंग्रेजी में)
हम इस लेख में उपरोक्त कुछ बिंदुओं का अध्ययन करेंगे। लेकिन उपरोक्त में से कुछ के लिए अलग लेख की आवश्यकता है, जैसे की tense में परिवर्तन, रिपोर्टिंग क्रिया में परिवर्तन। इसलिए, हम उनपर अलग-अलग लेखों में विस्तृत रूप से प्रकाश डालेंगे।
समुच्चयबोधक डालना (Insertion of Conjunction)
एक वाक्य को indirect speech में बदलते समय, 'अल्पविराम (comma)' और 'उल्टे अल्पविराम (inverted commas)' हटा दिए जाते हैं, और इसके बजाय किसी समुच्चयबोधक (जैसे 'that') का उपयोग किया जाता है।
Indirect speech में समुच्चयबोधक, reporting clause को रिपोर्ट किए गए भाषण (reported speech) के साथ जोड़ता है।
 नोट
नोटकभी-कभी समुच्चयबोधक (conjunction) 'that' छुपा हुआ (silent) होता है।
Indirect speech में हम जिस समुच्चयबोधक (conjunction) का उपयोग करेंगे, वह direct speech की reported clause में वाक्य के प्रकार पर निर्भर करेगा।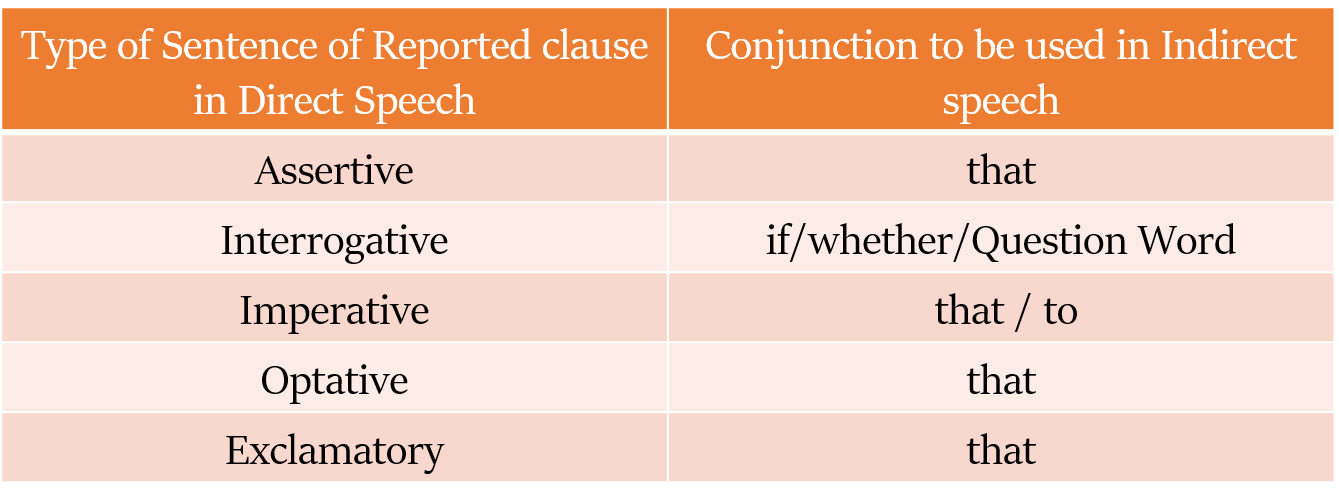
Person/Pronoun का परिवर्तन (Change in Person/Pronoun)
जब हम direct speech को indirect speech में बदलते हैं, तो हम जहां आवश्यक हो, सर्वनाम (pronouns) बदल देते हैं।
सर्वनाम (Pronouns) निम्नलिखित नियमों के अनुसार बदले जाते हैं:
\(1^{st}\) Person (I, we) reporting verb के Subject के अनुसार बदलता है।
\(2^{nd}\) Person (you) reporting verb के Object के अनुसार बदलता है।
\(3^{rd}\) Person (he, she, it, they) नहीं बदलता है।
 नोट
नोटआप इसे परिवर्णी शब्द (acronym) का उपयोग करके याद रख सकते हैं: S (\(1^{st}\)) O (\(2^{nd}\)) N (\(3^{rd}\))
- S - reporting verb का Subject
- O - reporting verb का Object
- N - कोई बदलाव नहीं
 नोट
नोटसर्वनाम (pronoun) का case नहीं बदला जाना चाहिए। उदाहरण के लिए, हम 'I' (subjective case) को ‘he’ (subjective case) में बदल सकते हैं, लेकिन ‘him’ (objective case) में नहीं।
आरेख:
इन सामान्य नियमों के अलावा, कुछ अपवाद और अतिरिक्त नियम हैं जिन्हें हमें ध्यान में रखना चाहिए।
अपवाद (Exceptions)
अपवाद 1
यदि reporting verb का subject 'he' या 'she' है, और उल्टे अल्पविराम के अंदर 'we' का उपयोग किया जाता है, तो सामान्य स्थिति में हम 'we' को 'they' में बदल देते हैं। हालाँकि, यदि उस कथन की रिपोर्ट करने वाले व्यक्ति (अर्थात वक्ता) को भी उस कथन में शामिल किया जाता है, तो हम 'we' नहीं बदलते हैं, अर्थात हम इसे वैसे ही छोड़ देते हैं।
Direct Speech: She said to me, "we are friends".
सामान्य स्थिति में हम 'we' को 'they' में बदल देंगे, reporting verb के subject के अनुसार।
Indirect Speech: She said to me that they are friends.
परन्तु, अगर रिपोर्ट करने वाला भी उसका दोस्त है, तो हम उसे वैसे ही छोड़ देते हैं।
Indirect Speech: She said to me that we are friends.
कभी-कभी, इस बात पर कोई अस्पष्टता नहीं होती है कि वक्ता को भी कथन में शामिल किया गया है या नहीं।
Direct Speech: My brother said to me, “we can’t change the habit of our father.”
Indirect Speech: My brother told me that we could not change the habit of our father.
अपवाद 2
अखबार, संगठन, आदि के मामले में हम 'we' को 'it' में बदल देते हैं।
Direct Speech: The New York Times said, “we are not responsible for this kind of error.”
Indirect Speech: The New York Times said that it was not responsible for that kind of error.
समय और जगह का परिवर्तन (Change in Time and Place)
यदि Reporting verb वर्तमान काल (present tense) में है - तो समय और स्थान से संबंधित शब्दों में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं किया जाता है|
यदि Reporting verb भूतकाल (past tense) में है - तो समय और स्थान से संबंधित शब्दों को बदल दिया जाता है।
समय या स्थान में निकटता व्यक्त करने वाले शब्दों को आम तौर पर दूरी व्यक्त करने वाले शब्दों में बदल दिया जाता है।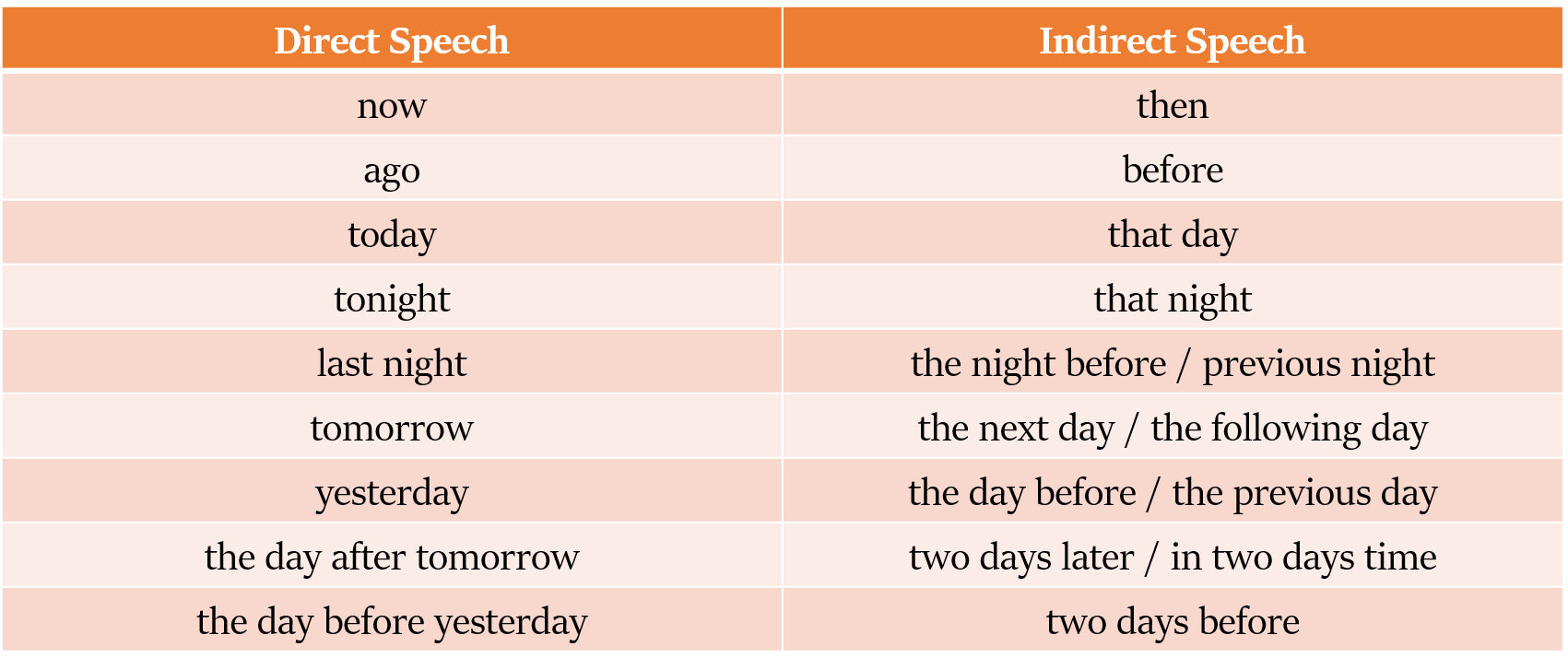

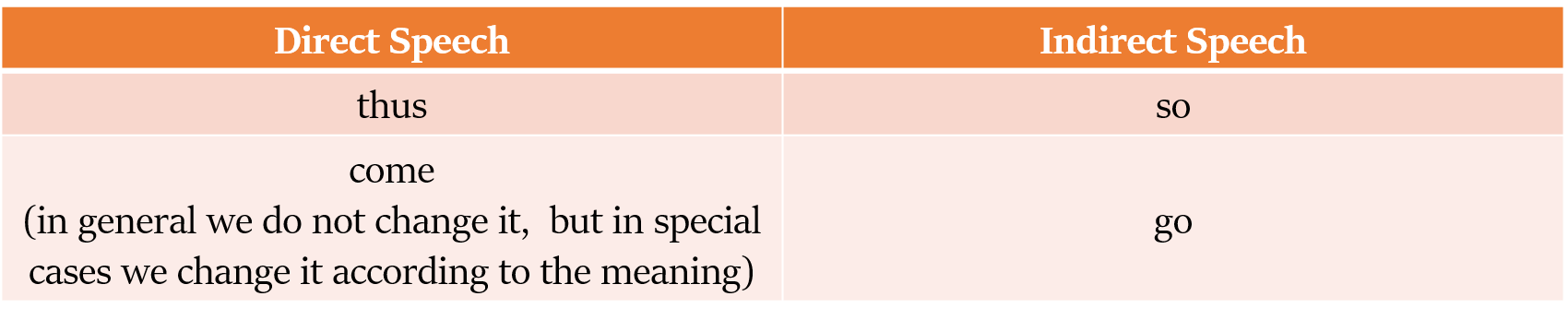
Modals का परिवर्तन (Change of Modals)
निम्नलिखित मोडल (modals) में कोई बदलाव नहीं किया जाता है:
should, would, could, might, ought to, used to
'I could meet you at the bar.'
He said that he could meet us at the bar.
'We might go fishing if we have spare time.'
They said they might go fishing if they have spare time.
Direct Speech को Indirect Speech में बदलते समय, हम निम्नलिखित परिवर्तन करते हैं:
may, can
- may – might
- can – could
She said, "I cannot help you at this time.“
She said that she couldn't help me at that time.
will
will (दूसरे और तीसरे person के साथ) → would/should
पहले, दूसरे या तीसरे person के साथ 'would' आ सकता है।
'should' केवल पहले person के साथ पसंद किया जाता है।
 अपवाद
अपवादइसलिए, हम जानते हैं कि 'will' आमतौर पर 'would' में बदल दिया जाता है, 'can' को 'could' में, और 'may' को 'might' में। परन्तु, इसके कुछ अपवाद भी हैं:
अपवाद 1
यदि reporting clause में क्रिया वर्तमान काल (present tense) में है, और जिस स्थिति की हम रिपोर्ट कर रहे हैं वह अभी भी मौजूद है या अभी भी भविष्य में हो सकती है → हम indirect speech में will, can, और may को तरजीह देते हैं।
'Careful! You will burn your hands!'
I warned him he would burn his hands. (स्थिति अब मौजूद नहीं है, इसलिए हमने 'would' का इस्तेमाल किया)
'I will be in Mewad at Deepawali.'
He tells me he will be in Mewad at Deepawali. (tells – present tense; स्थिति अभी भी मौजूद है या भविष्य में हो सकती है, इसलिए हमने 'will' का इस्तेमाल किया)
अपवाद 2
यदि reporting clause में क्रिया भूतकाल (past tense) में है, और जिस स्थिति की हम रिपोर्ट कर रहे हैं वह अभी भी मौजूद है या अभी भी भविष्य में हो सकती है → हम indirect speech में या तो 'would या will' का इस्तेमाल कर सकते हैं, या फिर 'can या could', या 'may या might' का।
'The situation can be resolved.'
They said the situation can/could be resolved. (said – past tense)
shall
shall (I/we के साथ आता है) → would/should
पहले, दूसरे या तीसरे person के साथ 'would' आ सकता है।
'should' केवल पहले person के साथ पसंद किया जाता है।
He said to me, "I shall come to meet you tomorrow."
He told me that he would come to meet me the next day.
 नोट
नोटshall (अनुरोध) → should (अनुरोध)
'should' सभी persons के साथ आता है, यदि अनुरोध (request) किया जा रहा है।
must
अवधारणा 1
यदि direct speech में, 'must' का उपयोग यह कहने के लिए किया गया है कि कुछ करना आवश्यक है → हम indirect speech में या तो 'must' या 'had to' का उपयोग कर सकते हैं ('had to' को प्राथमिकता दी जाती है)
'You must be home by 8 o'clock.'
He said I must / had to be home by 8 o'clock.
अवधारणा 2
यदि direct speech में, 'must' का उपयोग यह निष्कर्ष निकालने के लिए किया गया है कि कुछ हुआ, या यह कहने के लिए कि कुछ सच है (यानी जब हम निष्कर्ष निकालते हैं) → हम indirect speech में 'must' का उपयोग करते हैं (बजाय 'had to' के)
'I must be getting old.'
He said that he must be getting old.
mustn’t
यदि direct speech में, mustn't उपयोग किया गया है → हम indirect speech में mustn't का उपयोग करते हैं (didn't have to के बजाय)
'You mustn't kill John Connor.'
He warned me that I mustn't kill John Connor.
 नोट
नोटहम कभी-कभी indirect speech में modal verb का उपयोग करते हैं, भले ही direct speech में कोई modal verb नहीं था।
'You're not allowed to play here.'
He told me that I mustn't play there.
Miscellaneous
direct speech में सम्मान के शब्द ('Sir, 'Madam‘, 'Your Honour', आदि), indirect speech में 'respectfully' में बदल जाते हैं।
direct speech में स्नेह के शब्द ('Darling‘, 'Dear‘, 'My beloved', आदि), indirect speech में 'lovingly/affectionately' में बदल जाते हैं।
इनडायरेक्ट से डायरेक्ट में बदलना (Conversion from Indirect Speech to Direct Speech)
indirect speech को direct speech में बदलना बहुत आसान है, और आम तौर पर इसमें कोई विशेष कठिनाई नहीं होती है।
Indirect speech: As the salesman entered the society, he was met by a watchman, who asked him if he was a delivery boy.
Direct speech: As the salesman entered the society, he was met by a watchman, who asked, “Are you a delivery boy?”
Indirect speech: He asked how he could be of any help.
Direct speech: He said, “How can I be of any help?

अतिरिक्त पुस्तकें और उपकरण
यदि आप किताबों के माध्यम से सीखना पसंद करते हैं, या संदर्भ उद्देश्यों के लिए कुछ अच्छी अंग्रेज़ी व्याकरण किताबें चाहते हैं, तो आप हमारा यह लेख पढ़ सकते हैं|