डायरेक्ट कथन को इनडायरेक्ट कथन में परिवर्तित करने पर काल में परिवर्तन (Changes in Tenses while converting Direct Speech into Indirect Speech)

Overview
इस लेख में हम अंग्रेजी के एक महत्त्वपूर्ण अध्याय के बारे में जानेंगे - Changes in Tenses while converting Direct Speech into Indirect Speech, in Hindi (हिंदी में)
इस लेख में, हम अध्ययन करेंगे कि जब हम direct speech को indirect speech में परिवर्तित करते हैं तो हम काल (tenses) कैसे बदलते हैं।
 नोट
नोटइस अध्याय से सम्बंधित, अन्य विषयों के बारे में जानने के लिए आप हमारे निम्नलिखित लेख पढ़ सकते हैं:
- डायरेक्ट और इनडायरेक्ट कथन क्या होते हैं?
- डायरेक्ट कथन को इनडायरेक्ट कथन में बदलने के नियम
- घोषणात्मक वाक्यों को इनडायरेक्ट बनाने पर रिपोर्टिंग क्रिया में परिवर्तन
- प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों को इनडायरेक्ट बनाने पर रिपोर्टिंग क्रिया में परिवर्तन
- आदेशसूचक वाक्यों को इनडायरेक्ट बनाने पर रिपोर्टिंग क्रिया में परिवर्तन
- विस्मयादिबोधक और इच्छावाचक वाक्यों को इनडायरेक्ट बनाने पर रिपोर्टिंग क्रिया में परिवर्तन
जब रिपोर्टिंग क्रिया वर्तमान काल या भविष्य काल में हो (Reporting verb in Present tense or Future tense)
यदि reporting verb (या principal verb) वर्तमान काल या भविष्य काल में है, तो हम direct speech/reported speech के tense को नहीं बदलते हैं।
She says, “Mak was a teacher".
She says that Mak was a teacher. (Mak was a teacher - reported speech, tense में कोई बदलाव नहीं)
He will say, “I am not the culprit".
He will say that he is not the culprit. (he is not the culprit - reported speech, tense में कोई बदलाव नहीं)
जब रिपोर्टिंग क्रिया भूतकाल में हो (Reporting verb in Past tense)
जब reporting verb भूतकाल में होती है (और reported speech मुहावरा/वाक्यांश आदि नहीं है), direct/reported speech के सभी tenses संबंधित भूत काल में बदल जाते हैं। अर्थात्:
केस 1: Simple present (\(V_1\)/do/does) को Simple past (\(V_2\)/did) में बदल दिया जाता है।
केस 2: Simple past (\(V_2\)/did) को Past perfect (had + \(V_3\)) में बदल दिया जाता है।
केस 3: Past perfect (had + \(V_3\)) नहीं बदला जाता है।
 नोट
नोटआप निम्नलिखित क्रम को याद कर सकते हैं।
Simple present → Simple past → Past perfect → कोई बदलाव नहीं
केस 1: Simple present बन जाता है Simple past (Simple present becomes Simple past)
Simple present (\(V_1/V_{s/es}\)/do/does) बन जाता है Simple past (\(V_2\)/did).
प्रकार 1
‘am/is/are’ को ‘was/were’ में बदल दिया जाता है|
Direct speech: He said, “I am fine.” (I am fine – simple present tense)
Indirect speech: He said (that) he was fine. (he was fine – simple past tense)
प्रकार 2
‘it is + time + subject + \(V_2\)’ को ‘it was + time + subject + \(V_2\)’ में बदल दिया जाता है|
Direct speech: He said, “It is time we left.” (It is time – simple present tense)
Indirect speech: He said (that) it was time we left. (it was time – simple past tense)
प्रकार 3
‘subject + has/have + to + \(V_1\)’ को ‘subject + had + to + \(V_1\)’ में बदल दिया जाता है|
Direct speech: He said, “I have to study.” (I have to study – simple present tense)
Indirect speech: He said (that) he had to study. (he had to study – simple past tense)
प्रकार 4
‘subject + do/does + not + have + to + \(V_1\)’ को ‘subject + did + not + have + to + \(V_1\)’ में बदल दिया जाता है|
Direct speech: He said, “I do not have to study.” (I do not have to study – simple present tense)
Indirect speech: He said (that) he did not have to study. (he did not have to study – simple past tense)
प्रकार 5
‘do/does + subject + have + object’ को ‘if/whether + subject + had + object’ में बदल दिया जाता है|
Direct speech: He said, “Do you have a pen?” (Do you have a pen – simple present tense)
Indirect speech: He asked (that) whether I had a pen. (I had a pen – simple past tense)
प्रकार 6
‘do/does + subject + have + to + \(V_1\)’ को ‘if/whether + subject + had + to + \(V_1\)’ में बदल दिया जाता है|
Direct speech: He said, “Do I have to play?” (Do I have to play– simple present tense)
Indirect speech: He asked (that) whether he had to play. (he had to play – simple past tense)
केस 2: Simple past becomes Past perfect
Simple past (\(V_2\)/did) को Past perfect (had + \(V_3\)) में बदल दिया जाता है|
प्रकार 1
‘was/were’ को ‘had been’ में बदल दिया जाता है|
Direct speech: He said, “I was an engineer.” (I was an engineer – simple past tense)
Indirect speech: He said (that) he had been an engineer. (he had been an engineer – past perfect tense)
प्रकार 2
‘\(V_2\)’ को ‘had \(V_3\)’ में बदल दिया जाता है|
Direct speech: He said, “I saw Mark.” (I saw Mark – simple past tense)
Indirect speech: He said (that) he had seen Mark. (he had seen Mark – past perfect tense)
प्रकार 3
‘Did + subject + have + to’ को ‘if/whether + subject + had had + to + \(V_1\)’ में बदल दिया जाता है|
Direct speech: He said, “Did you have to play?” (Did you have to play? – simple past tense)
Indirect speech: He asked (that) whether he had had to play. (he had had to play – past perfect tense)
प्रकार 4
‘had + to + \(V_1\)’ को निम्नलिखित में से किसी में बदल दिया जाता है:
‘had had + to + \(V_1\)’ (इसको तरजीह दी जाती है) या
‘had + to + \(V_1\)’ (अर्थात कोई परिवर्तन नहीं)
Direct speech: He said, “I had to work.” (I had to work – simple past tense)
Indirect speech: He said (that) he had had to work. (he had had to work – past perfect tense, इसको ज्यादा तरजीह दी जाती है)
Indirect speech: He said (that) he had to work. (he had to work – simple past tense, इसको कम तरजीह दी जाती है)
प्रकार 5
‘had + noun’ को निम्नलिखित में से किसी में बदल दिया जाता है:
- ‘had had + noun’ (इसको तरजीह दी जाती है) या
- ‘had + noun’ (अर्थात कोई परिवर्तन नहीं)
Direct speech: He said, “I had a bat.” (I had a bat – simple past tense)
Indirect speech: He said (that) he had had a bat. (he had had a bat – past perfect tense, इसको ज्यादा तरजीह दी जाती है)
Indirect speech: He said (that) he had a bat. (he had a bat – simple past tense, इसको कम तरजीह दी जाती है)
केस 3: Past perfect को नहीं बदला जाता है
Past perfect (had + \(V_3\)) को नहीं बदला जाता है।
Direct speech: He said, “I had played cricket with Mark.” (I had played cricket – past perfect tense)
Indirect speech: He said (that) he had played cricket with Mark. (he had played cricket – past perfect tense)
आइए, कुछ और मामले देखते हैं।
केस 4: Present continuous बन जाता है Past continuous
Present continuous (is/am/are) बन जाता है Past continuous (was/were)
Direct speech: He said, “I am playing cricket.” (I am playing cricket – present continuous tense)
Indirect speech: He said (that) he was playing cricket. (he was playing cricket – past continuous tense)
केस 5: Past continuous बन जाता है Past perfect continuous
Past continuous (was/were) बन जाता है Past perfect continuous (had been \(V_4\))
Direct speech: He said, “I was playing cricket with Mark.” (I was playing cricket – past continuous tense)
Indirect speech: He said (that) he had been playing cricket with Mark. (he had been playing cricket – past perfect continuous tense)
केस 6: Past perfect continuous को नहीं बदला जाता है
Past perfect continuous (had been \(V_4\)) को नहीं बदला जाता है|
Direct speech: He said, “I had been playing cricket with Mark.” (I had been playing cricket – past perfect continuous tense)
Indirect speech: He said (that) he had been playing cricket with Mark. (he had been playing cricket – past perfect continuous tense)
 नोट
नोटआप निम्नलिखित क्रम को याद कर सकते हैं।
Present continuous → Past continuous → Past perfect continuous → कोई परिवर्तन नहीं
आइए, कुछ और मामले देखते हैं।
केस 7: Present perfect बन जाता है Past perfect
Present perfect (has/have + \(V_3\)) बन जाता है Past perfect (had + \(V_3\)).
Direct speech: He said, “I have played cricket.” (I have played cricket– present perfect tense)
Indirect speech: He said (that) he had played cricket. (he had played cricket – past perfect tense)
Direct speech: He said, “I have seen the episode before.” (I have seen – present perfect tense)
Indirect speech: He said (that) he had seen the episode before. (he had seen – past perfect tense)
केस 8: Present perfect continuous बन जाता है Past perfect continuous
Present perfect continuous (has/have been \(V_4\)) बन जाता है Past perfect continuous (had been \(V_4\))
Direct speech: He said, “I have been playing cricket.” (I have been playing cricket– present perfect continuous tense)
Indirect speech: He said (that) he had been playing cricket. (he had been playing cricket – past perfect continuous tense)
केस 9: Past perfect और Past perfect continuous को नहीं बदला जाता है
Past perfect और Past perfect continuous (had been \(V_4\)) को नहीं बदला जाता है|
Direct speech: He said, “I had played cricket.” (I had played cricket – past perfect tense)
Indirect speech: He said (that) he had played cricket. (he had played cricket – past perfect tense)
Direct speech: He said, “I had been playing cricket.” (I have been playing cricket– past perfect continuous tense)
Indirect speech: He said (that) he had been playing cricket. (he had been playing cricket – past perfect continuous tense)
 नोट
नोटआप निम्नलिखित क्रम को याद कर सकते हैं।
Present perfect / Present perfect continuous → Past perfect / Past perfect continuous → कोई बदलाव नहीं
सामान्य नियमों के अपवाद (Exceptions to general rules)
अपवाद 1
स्थायी स्थिति या सार्वभौमिक सत्य के मामले में Tenses:
यदि reporting verb 'अतीत' में है, और रिपोर्ट किया गया भाषण (reported speech) अभी भी प्रासंगिक है (यानी एक सार्वभौमिक सत्य/वाक्यांश/मुहावरे/आदतन क्रिया/ऐतिहासिक तथ्य)।
ऐसे मामले में, हम अक्सर चुन सकते हैं कि मूल tenses को वैसे ही रखना है, या उन्हें बदलना है।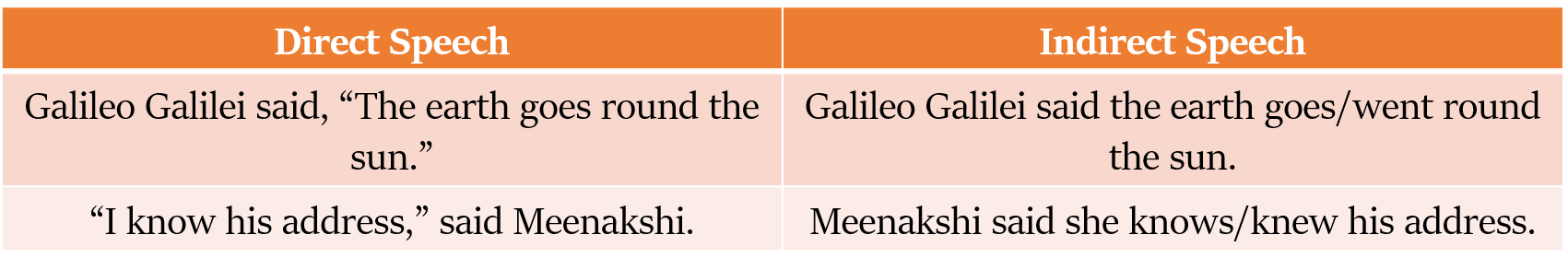
यदि reporting verb भूत काल में है, तो हम निम्नलिखित मामलों में reported clause में भूत काल प्रयोग करना पसंद करते हैं (वर्तमान काल के बजाय):
- हमें यकीन नहीं है कि हम जो रिपोर्ट कर रहे हैं वह अनिवार्य रूप से सच है
- वह स्थिति हो सकता है की अब मौजूद न हो
- जब हम निष्पक्ष रूप से रिपोर्ट कर रहे हों (reporting objectively)
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों की तुलना करें:
Jim told me that he has three cars. (told – reporting verb भूत काल में है; has – reported clause की क्रिया वर्तमान काल में है; यह बताता है कि जो रिपोर्ट किया जा रहा है वह वास्तव में सच है, यानी Jim के पास तीन कारें हैं।)
Jim told me that he had three cars. (told – reporting verb भूत काल में है; had – reported clause की क्रिया भूत काल में है; यह बताता है कि जो रिपोर्ट किया जा रहा है वह या तो सच नहीं है, या वह स्थिति अब उपस्थित नहीं है, यानी या तो Jim के पास कभी तीन कारें थीं ही नहीं, या उसके पास कभी तीन कारें थीं, लेकिन अब नहीं।)
 नोट
नोटयदि reporting verb 'वर्तमान' में है, और हम एक स्थायी स्थिति या सार्वभौमिक सत्य की रिपोर्ट कर रहे हैं, तो भी हम रिपोर्ट किए गए खंड (reported clause) की क्रिया के लिए वर्तमान काल का उपयोग करते हैं।
Aanya thinks that she spent about 15 minutes on a typical meeting with a customer. (गलत)
Aanya thinks that she spends about 15 minutes on a typical meeting with a customer. (सही; thinks – reporting verb वर्तमान काल में है; spends – reported clause की क्रिया भी वर्तमान काल में है)
British scientists claim that they developed a new vaccine for Covid-19. (गलत)
British scientists claim that they have developed a new vaccine for Covid-19. (सही; claim – reporting verb वर्तमान काल में है; have developed – reported clause की क्रिया भी वर्तमान काल में है)
अपवाद 2: तत्काल कार्रवाई/क्रिया-प्रतिक्रिया के मामले में Tenses
तत्काल क्रिया (instant action) या क्रिया-प्रतिक्रिया (action–reaction) के मामले में, tense में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं होगा।
Direct Speech: The event manager said, “As soon as Katy Perry started dancing everybody stood in praise.”
Indirect Speech: The event manager said that as soon as Katy Perry started dancing everybody stood in praise.
Direct Speech: Jim said to Dwight, “when you opened the window, the wind came in.”
Indirect Speech: Jim told Dwight that when he opened the window, the wind came in.
अपवाद 3: अतीत में चल रही दो कार्रवाइयों के मामले में Tenses
भूतकाल में चल रही दो क्रियाओं (two ongoing actions) के मामले में, tense में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं होगा।
Direct Speech: Monika said, “while I was playing badminton some boys and girls were booing me”.
Indirect Speech: Monika said that while she was playing badminton some boys and girls were booing her. (हमने सर्वनाम बदल दिया है, लेकिन tense नहीं)
Direct Speech: Mragank said to Mayank, “while I was looking at you, you were looking at someone else.”
Indirect Speech: Mragank told Mayank that while he was looking at him, he was looking at someone else.
अपवाद 4: सहायक क्रियाओं के मामले में Tenses (Tenses in case of helping verbs)
मोडल क्रियाओं (modal verbs) के मामले में, tense में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं होगा।
Direct Speech: He said, “There used to be a small school near my house.”
Indirect Speech: He said that there used to be a small school near his house. (हमने सर्वनाम बदल दिया है, लेकिन tense नहीं)
Direct Speech: Parshuram said, “I would rather die than give the secret away to enemy.”
Indirect Speech: Parshuram said that he would rather die than give the secret away to enemy.
 नोट
नोटयहाँ कुछ मोडल क्रियाएँ (modal verbs) दी गयी हैं:
will, shall, would, should, could, might, used to, ought to, need not, dare not etc.
अपवाद 5: कुछ संरचनाओं के मामले में काल (Tenses in case of certain structures)
निम्नलिखित पैटर्न के मामले में, tense में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं होगा।
पैटर्न 1
Subject + had + \(V_3\) + ........ + before + Subject + \(V_2\) + .............
Direct Speech: They said, “We had played tennis ball cricket for some time before we played leather ball cricket”.
Indirect Speech: They said that they had played tennis ball cricket for some time before they played leather ball cricket.
पैटर्न 2
Subject + \(V_2\) + ...........+ after + Subject + had + \(V_3\) +..............
Direct Speech: They said, “We played leather ball cricket after we had played tennis ball cricket for some time”.
Indirect Speech: They said that they played leather ball cricket after they had played tennis ball cricket for some time.
पैटर्न 3
By the time + Subject + \(V_2\) + .........+ Subject + had + \(V_3\) + ............
Annie said to Eva, “By the time you left Italy, I had married your friend.”
Annie told Eva that by the time she left Italy, she had married her friend.
पैटर्न 4
If + Subject + had + \(V_3\) + .......... + Subject + would + ........ + have + \(V_3\) + .....
Anand said, “If you had reached there on time, I would have been saved.”
Anand said that if I had reached there on time, he would have been saved. ('I' will be used, not 'he')
पैटर्न 5
If + Subject + \(V_2\) + ....... + Subject + would + ......... + \(V_1\) + ......
Anand said, “If you were a teacher, I would respect you.”
Anand said that if I were a teacher, he would respect me. ('I' will be used, not 'he')

अतिरिक्त पुस्तकें और उपकरण
यदि आप किताबों के माध्यम से सीखना पसंद करते हैं, या संदर्भ उद्देश्यों के लिए कुछ अच्छी अंग्रेज़ी व्याकरण किताबें चाहते हैं, तो आप हमारा यह लेख पढ़ सकते हैं|